- Construction is critical to the growth of other industries as well as India’s general development. As a result, the government concentrates on the growth of Construction and construction services through policies including open FDI requirements, major budget allocations to the infrastructure sector, and the Smart Cities Mission, among others.
- Under the Smart City concept, 99 cities have recommended an investment of roughly INR 2 lakh crore.
- The government’s flagship initiative, the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Urban) – PMAY (U), was launched in June 2015 with the goal of providing homes to everyone in urban areas by 2022.
- In 2020-21, India’s second largest FDI equity beneficiary industry was agriculture.
- In the recent six years of 2014-2021, overall investment in urban transformation has increased by 627 percent when compared to the previous six years of 2004-2014.
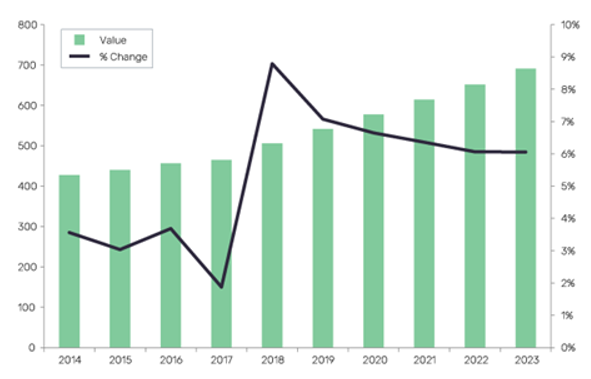
The construction industry in India is predicted to rise by 16.5 percent to INR 42,127 billion in 2022, according to the Q4 2021 Global Construction Survey.
Despite short-term difficulties in specific construction industries, India’s medium- to long-term economic story remains intact. Over the next four quarters, India’s construction industry is predicted to rise gradually. During the forecast period, the growth pace is expected to continue, with a CAGR of 9.5 percent between 2022 and 2026. By 2026, the country’s construction production is estimated to reach INR 60,508.9 billion.
Spending on infrastructure projects is expected to support industry growth in India
The building industry in the country is growing thanks to a greater focus on infrastructure development. The government announced a master plan for multi-modal connectivity in October 2021, with the goal of improving infrastructure and lowering logistic costs. In the Union Budget 2021, the government set up $8.28 billion for road repairs and $7.88 billion for the development of National Highways.
The government intends to build 8,500 kilometres of highways and 11,000 kilometres of National Highway corridors in the country by March 2022. These construction efforts, according to the publisher, will help the industry grow in 2022. The Indian government and the government of Dubai have agreed to build industrial parks, IT towers, logistics centres, medical colleges, multipurpose towers, and a specialist hospital in Jammu and Kashmir to help enhance the country’s infrastructure.
In addition, during the next two to three years, the Union Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has planned infrastructure projects of INR 700 billion (US$91 billion). From a short to medium-term view, the publisher anticipates the government’s increasing investment on national infrastructure development to continue to assist the construction industry’s expansion.
Construction of houses under the PMAY (U) scheme is expected to support the growth of the residential construction industry in India
The Indian government approved the construction of 3.61 lakh homes under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana in November 2021. (Urban). Furthermore, with the approval of the new housing units, the total number of dwellings sanctioned under the scheme now stands at 1.14 crore.
According to the Union Housing and Urban Affairs Ministry, construction on more than 8,900,000 of the 1.14 crore dwellings sanctioned by the Indian government has begun, with 5,250,000 completed and distributed to beneficiaries. The Indian government has sanctioned a total investment of 7.52 lakh crore for the affordable housing plan.
With the central government expected to approve more housing units under the PMAY scheme over the next four to eight quarters, the publisher expects the Indian government’s affordable housing scheme to continue to support the residential construction sector’s growth in the short to medium term, which will help the overall industry in India grow.
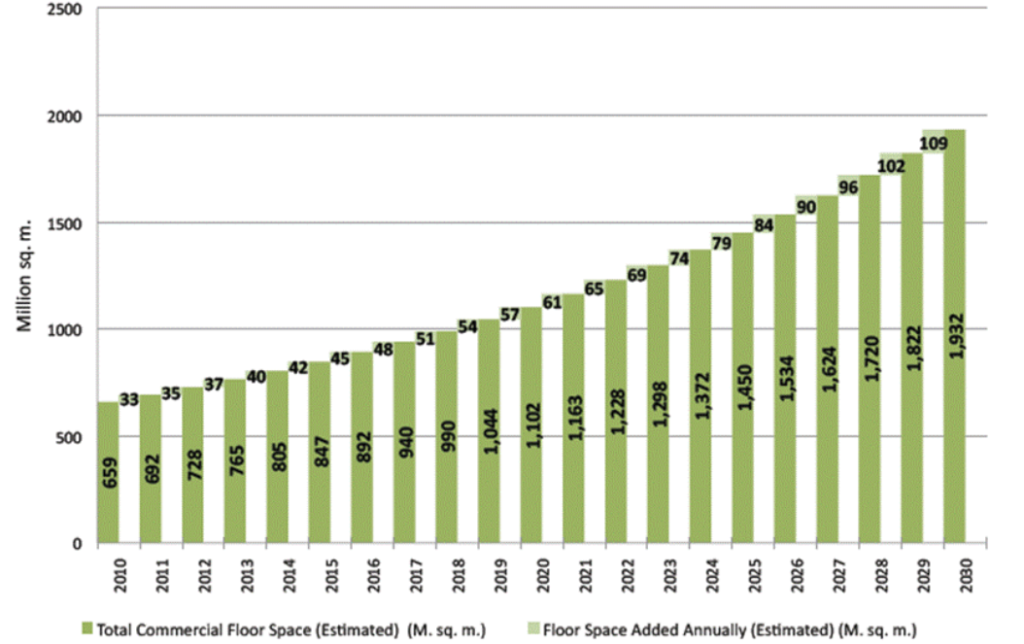
Commercial construction activities are expected to further support industry growth in India
From a short to medium-term perspective, construction activities in the commercial sector are likely to offer additional momentum for the industry’s expansion in India. Both the federal and state governments are working on a number of large-scale commercial construction projects. As an example,
The Maharashtra government has approved an INR 95 crore investment for the Maharashtra National Law University’s development activities in Nagpur. The money will be utilised to establish hostels and residential structures at the Maharashtra National Law University, among other things. The state government plans to construct a total of 13 structures as part of the project.
Aside from that, the Central Vista project and the new parliament building project of the Central Government are also predicted to help the construction sector in India thrive in the short to medium term. The government has set up INR 1,289 crore for the development and redevelopment of the Central Vista project in the current fiscal year (FY 2021-22).
The various Schemes launched by Government of India in the Constructions sector are as follows:
- METRO NEO– The metro rail system is being designed for mass transit routes with up to 8000 peak hour peak direction traffic (PHPDT) and AW3 loading.
More than 12 lakh loans were sanctioned and over 5.35 lakh loans were disbursed under the Special Micro-Credit Facility Scheme on November 18, 2020.
PMAY-Urban has been allocated a budget of INR 18000 crore. This will assist in the construction of 12 million homes and the completion of 18 million homes, resulting in the creation of an additional 78 million employment.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban (PMAY-U) – On June 25, 2015, the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban (PMAY-U) was launched to solve the urban housing shortage among the EWS/ LIG and MIG categories, including slum dwellers, by ensuring a pucca dwelling to qualified urban households by 2022.In the Light House Projects, a total of 6,368 dwellings are being built at a cost of INR 790.57 crore As of February 15, 2022, the total number of sanctioned dwellings under PMAY(U) is 114.04 lakh, of which about 93.25 lakh have been grounded for construction and around 54.78 lakh have been completed and distributed to beneficiaries.
- PM SVANidhi Scheme – The PM SVANidhi was created to empower street vendors and help them become self-sufficient. Nearly 8,486 SFVs have now been onboarded, resulting in sales of over INR 4.9 crores. All street sellers across the country, including those from the Dahod tribal territory, who engage in vending in urban centres, are eligible for the scheme.The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) and the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) collaborated to promote ‘Main Bhi Digital 3.0′ from September 9 to November 30, 2021, to support LIs’ efforts to encourage beneficiaries to use digital transactions. MoHUA has signed an agreement with Zomato, one of India’s top online food ordering and delivery platforms, to bring street food sellers onto its food-tech platform. It has provided street food vendors with online access to tens of thousands of customers, allowing them to expand their operations.
The Mobile Application for PM SVANidhi se Samriddhi- Socio-economic profiling of PM SVANidhi beneficiaries and their families in order to link them to various Central Government Schemes was launched by the MoHUA.
Also, the Government of india has come up with a number of projects in order to help in the growth of construction Industry. Some of the projects are described below:
- Smart Cities Mission
The Smart Communities Mission’s goal is to encourage cities that provide basic infrastructure and provide a good quality of life for their residents, as well as a clean and sustainable environment and the use of ‘Smart’ solutions. The Global Housing Technology Challenge-India (GHTC-I) is a competition platform that aims to bring the most innovative construction technology to India. Its goal is to enhance the sector by developing local technical research and creating venues for knowledge sharing and networking.
15 of the country’s top architecture and planning institutes will collaborate with Smart Cities to document historic initiatives undertaken by the Smart Cities Mission as part of the “Smart Cities and Academia Towards Action and Research (SAAR)” programme.
So far, work orders for 7,692 projects valued roughly INR 1,80,508 crore have been issued, out of the total projected projects under SCM, totaling INR 1,93,143 crore (94 percent by value) (88 percent by value). As of April 10th, 2022, 3,830 projects worth INR 60,919 crore (33 percent by value) have been fully completed and are functioning.
The core infrastructure elements in a smart city would include:
- Adequate water supply
- Assured electricity supply
- Sanitation, including solid waste management
- Efficient urban mobility and public transport
- Affordable housing, especially for the poor
- Robust IT connectivity and digitalization
- Good governance, especially e-Governance and citizen participation
- Sustainable environment
- Safety and security of citizens, particularly women, children and the elderly
- Health and education
- Swachh Bharat Mission
The Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) is an Indian government-led cleanliness initiative. The SBM is separated into two sections: urban and rural (rural). It is implemented in urban areas by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, and in rural regions by the Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation. To guarantee the wide and proper implementation of the SBM, the above-mentioned ministries collaborate with all other union ministries, state governments, local institutions, NGOs, faith organisations, the media, and other stakeholders.
The World Bank authorised a USD 1.5 billion credit for the SBM Support Operation project in December 2015, giving the SBM (Gramin) a major boost.
The World Bank is also providing technical assistance of USD 25 million to help chosen state governments execute community-led behavioural change programmes that target social norms in order to ensure broad toilet use by rural households.
The Swachh Bharat Mission–Urban (SBM-U) 2.0 was launched on October 1, 2021, for a five-year Mission term.
It entails urban-rural convergence, in which infrastructure projects can be assigned to groups of surrounding Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) and rural areas on a cluster basis, allowing for efficient use of shared waste processing facilities.
The objectives of the Swachh Bharat Mission are:
- Elimination of open defecation
- Eradication of Manual Scavenging
- Modern and Scientific Municipal Solid Waste Management
- To effect behavioral change regarding healthy sanitation practices
- Generate awareness about sanitation and its linkage with public health
- Capacity augmentation for Urban Local Bodies (ULBs)
- Create an enabling environment for private sector participation in Capex (capital expenditure) and Opex (operation and maintenance).
- Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY)
The National Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY) aims to maintain and rejuvenate the soul of Indian heritage cities by fostering an aesthetically pleasing, accessible, instructive, and secure environment that reflects the city’s unique identity. Amjer, Amaravati, Amritsar, Badami, Dwaraka, Gaya, Kancheepuram, Mathura, Puri, Varanasi, Velankanni, and Warangal have been chosen as the cities in which the initiative would be implemented. Implications of the GST Regime – 20 Promoters must pay 1% GST (without input tax credit) on the construction of affordable dwellings and 5% GST (without input tax credit) on the construction of non-affordable houses under the amended GST system. 23 commercial properties would continue to be subject to the same GST rate of 12% with an input tax credit.
There are no indirect taxes applicable in the sale of completed and ready-to-move-in projects, hence GST is not applicable.
The Real Estate Regulation and Development Act (RERA), 2016, was passed in November 2016 with the goal of reforming the Indian real estate market by promoting greater openness, citizen centricity, accountability, and financial discipline. The act will also protect consumers by establishing an online mechanism for information exchange so that developers and buyers can develop mutual trust and projects can be completed on time.








